Surgical procedures:
Impingement:
Fraying of articular or bursal surface of rotator cuff, subacromial-subdeltoid bursitis, acromioclavicular arthritis, fraying of coracoacromial ligament at its attachment to anteroinferior surface of the acromion
Arthroscopic subacromial decompression - method of choice for treatment of impingement, consists of resection of coracoacromial ligament, anterior and posterior acromion, acromioclavicular joint osteophytes,
Mumford procedure - resection of distal clavicle and increaing the ACJ space by 1-2 cm
Rotator cuff tears:
Partial bursal-sided tears associated with type 2 or 3 acromion or subacromial enthesophyteare tretaed with arthroscopic subacromial decompression and debridement.
Partial articular-sided tears not involving more than 2/3 of tendon thickness are treated with debridement with or without anterior acromioplasty.
Full-thickness tears usually need open surgery
Instability:
Capsulolabral complex and glenohumeral ligaments are treated with open surgerical reconstructions, which primarily restrict external rotation
Bankart procedure: Repair of inferior GHL with 3 suture anchors through holes drilled in the bone at approximate 3-, 4-, and 5-o’clock
Putti-Platt procedure: Shortening of anterior capsule and subscapularis
Magnusson-Stack procedure: Subscapularis from lesser tubercle to greater tubercle
Brestow-Helfet procedure: Corocoid process attachments to scapular neck
Bone-block osteotomy: Anterior bone block
Neer inferior capsular shift: inferior capsule moved superiorly
Post operative MR :
Fluid in subacromial-subdeltoid space is a nonspecific postoperative finding
Subacromial decompression:
Flat acromion with slightly tapered configuration
Decreased signal of acromion on T1 and T2 due to fibrosis
Change in the appearance of coracoacromial arch
Acromioclavicualr widening
Rotator cuff repair:
Int-to-low signal tendon (fibrosis)
Regular or irregular
Instability:
Capsular thickening
Bankart repair - paramagnetic anchor track artefacts in anterior glenoid bone and reattachment of the capsulolabral complex to glenoid margin
Putti-Platt procedure - thickening of subscapularis tendon at lesser tubercle
Bristow-Helfet procedure - alterations in coracoid process and anterior glenoid margin
Complications:
Intraoperative: acromial fracture, dehiscence of deltoid, axillary nerve injury (denervation of deltoid and teres minor), failure to preserve coracoacromial arch
Early: hematoma, infection, septic arthritis, avulsion of tendons or capsular structures (physiotherapy related)
Late:recurrent tear of tendons and capsulolabral structures, hardware displacement, heterotopic ossification, synovitis, frozen shoulder
References:
Mohana-Borges AVR et al. MR Imaging and MR Arthrography of the Postoperative Shoulder: Spectrum of Normal and Abnormal Findings. Radiographics. 2004;24:69-85
Image Gallary:
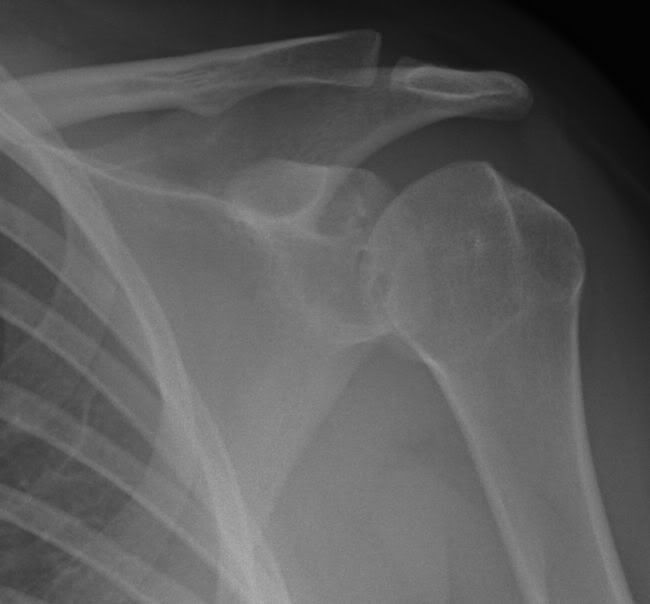
Anchor sutures 1:
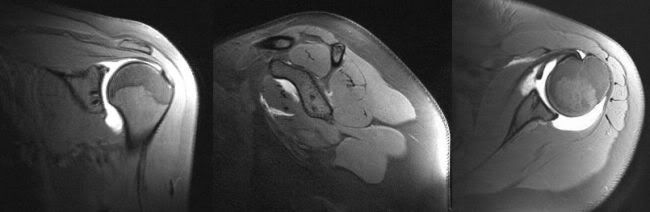
Anchor sutures 2:
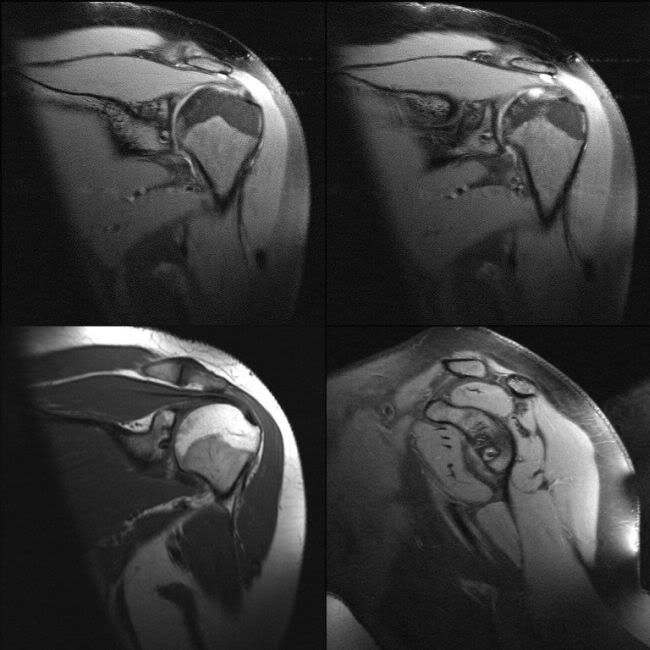
Anchor sutures plain film: